A new ground-breaking report from the International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA) provides clear direction on how to advance storage systems as part of the infrastructure for a sustainable energy future. Renewables and Electricity Storage, released today on the side lines of IRENA’s ninth Council meeting, prioritizes 14 action items across five priority areas where governments and industry can work together to facilitate the development of policies on electricity storage for renewables. The report is part of IRENA’s REmap 2030 program.
With solar and wind installation breaking new records each year, countries with ambitious plans for these renewable power-generation technologies must consider the best ways to integrate variable renewables onto the grid. Electricity storage is a key option available to manage variability and ensure reliable, round-the-clock supply. Declining costs and improving capacities have made batteries and other storage technologies increasingly practical for upgrading existing power systems.
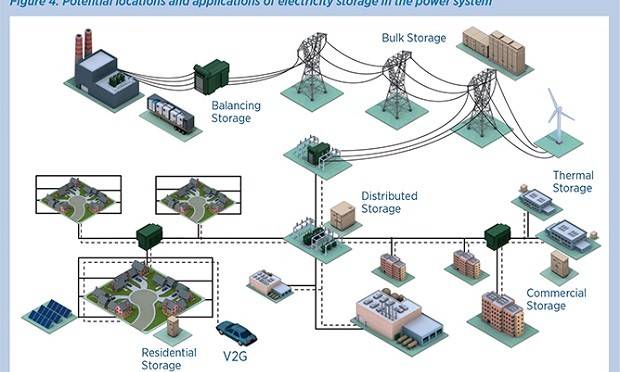
In the short term, battery storage can aid the transition from diesel-based generator sets to renewable options for isolated systems, such as on islands or in remote areas. For larger systems, pumped-storage hydropower remains a key technology supporting the integration of variable renewables. In the longer term, the coupling of storage technologies to rooftop solar photovoltaic (PV) panels or wind turbines could revolutionise electricity production, facilitating localised power supply and challenging utilities’ existing revenue and grid-management models.
Renewables and Electricity Storage, a technology roadmap prepared by the International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA), indicates priorities and points out specific actions where governments, industry and other stakeholders to work together to advance storage systems as part of the infrastructure for a sustainable energy future, with renewable sources and technologies dominating the power sector.
The technology roadmap was released before an industry audience at Intersolar in Munich, Germany, on 9 June 2015. It came as the latest component of REmap 2030, IRENA’s global roadmap to double the share of renewables in the energy mix in time to avert catastrophic climate change.
To avoid the worst effects of climate change and accelerate sustainable energy transformation and economic growth, IRENA’s REmap 2030 report finds the share of renewables in the electricity sector must double to 45 per cent by 2030. To do so, an estimated 150 GW of battery storage and 325 GW of pumped-storage hydroelectricity will be needed, making storage a vital element in the expansion of renewable energy.
“Now is the time to think about integrating large-scale battery storage into the global energy system,” said IRENA Director-General Adnan-Z Amin. “This roadmap is a starting point for all policy makers seeking to integrate greater storage capabilities, which is necessary to ensure the world is ready for the next phase of growth for renewable power systems.”
The five priority areas identified include electricity storage to support renewables in islands and remote areas, consumer-located storage for self-consumption in countries with high shares of rooftop solar PV systems, generator and grid-located storage for countries with grid infrastructure constraints and system analysis tools for countries preparing to transition their power sector towards renewables.
The roadmap is the product of four stakeholder workshops involving more than 200 electricity storage experts from 50 countries.
“The value of this roadmap is that it brought together policy makers from across the globe with the leading industry experts and academics,” said Chairperson of the Global Energy Storage Alliance Janice Lin. “At every workshop, we were asked to prioritize and refine our assessments. The roadmap is truly a product of international cooperation.”
http://www.irena.org/DocumentDownloads/Publications/IRENA_REmap_Electricity_Storage_2015.pdf